
How to Choose the Right Zinc Oxide Supplier for Safety and Quality
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is perhaps the most widely used chemical in industry today, with applications ranging from pharmaceuticals to ceramics, rubber, and semiconductors. Given its use in end-consumer goods and technology, ZnO quality standards must be directly aligned with industry-wide standards for safety, legislation, and performance. Choosing the appropriate ZnO supplier is thus a multi-step process in which chemical requirements, knowledge, and quality standards must be combined to enable the supplier to support long-term sustainability efforts.
1. Selecting the Right Grade and Standard
The key to a sound supplier partnership is first to verify which quality of zinc oxide is appropriate for your formulation’s intended use. Pharmaceuticals need suppliers that meet the US Pharmacopeia (USP) monograph standards for a 99.0% ZnO assay, with tests for identification, heavy metals, and loss on ignition. The Food/Nutrition industry’s standards would be more appropriate in relation to the Food Chemical Codex (FCC), which sets purity levels for use and ingestion standards.
Cosmetic makers rely on ISO 22716, the Good Manufacturing Practices guideline for personal care products, with a special focus on microbial control. Industrial applications in paint, rubber, etc., followed the ASTM D79 guideline regarding performance standards for ZnO in its pigment grade. It is essential to look for vendors who prioritize these guidelines in their ingredient choices for international market acceptability.
2. Evaluating the Supplier’s Quality Management System
A strong chemical specification is meaningless without a sound quality management system behind it. Suppliers should maintain ISO 9001 certification for process consistency and ISO 14001 for environmental responsibility. For sensitive applications like cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, the facility should also implement GMP-aligned operations, including batch segregation, validated methods, and regular internal audits.

Transparency is also essential. The qualified supplier should provide a Certificate of Analysis (CoA) for each shipment, including test results and the reference methods used. They should also maintain samples for each shipment and have a recall procedure in place. Suppliers who demonstrate transparency and make process changes in accordance with a change control policy show a level of trustworthiness in quality, which is required for sustained quality levels.
3. Ensuring Purity and Controlling Impurities
Despite the apparent purity, other contaminants present in small amounts could pose significant safety or performance concerns for zinc oxide. Heavy metal contaminants such as lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), arsenic (As), and mercury (Hg) need to be closely screened using ICP-MS or ICP-OES. Acceptable levels depend on the use, but generally need to meet the standards of the worldwide compendium.

Other key factors include soluble salts, acid-insoluble substances, and loss on ignition, as these affect chemical stability. In addition to the mentioned tests, microbial limits for external or oral preparations would also need to be tested in accordance with ISO 22716 protocols. A reputable supplier would ideally provide detection limits for testing to ensure testing accuracy.
Table 1, shown below, summarizes a typical incoming quality control (QC) test plan that can be adapted for different industrial needs. It includes analytical techniques such as titrimetric assays, ICP-OES for heavy-metal analysis, XRD for crystalline-phase identification, and BET surface-area analysis for physical characterization.
Table 1. Example Incoming QC Test Plan
| Test | Method (Example) | Typical Frequency |
| Assay (ZnO, %) | Titrimetric / ICP-OES | Each lot |
| Heavy metals (Pb, Cd, As, Hg) | ICP-MS / ICP-OES | Each lot |
| Moisture / Loss on ignition | Thermogravimetric | Each lot |
| Particle size (D₅₀) | Laser diffraction | Quarterly validation |
| BET surface area | Nitrogen adsorption | Quarterly validation |
| Crystal phase | Powder XRD | Each lot |
| Soluble salts | Ion chromatography | Each lot |
| Microbial limits | ISO 22716-aligned SOP | Each lot (risk-based) |
4. Particle Properties and Functional Behavior
Some physical properties associated with zinc oxide that influence its reactivity in different applications include particle size, shape, and surface area. Nano-sized zinc oxide is employed in the formulation of sunscreen lotions for its protective properties against ultraviolet radiation from the sun. In contrast, others with relatively large particles are used in rubber vulcanization and ceramics.
Deliverables from the suppliers would include particle size distributions from laser diffraction analyses, specific surface area data from BET analyses, X-ray diffraction (XRD) to substantiate the correct wurtzite structure [8], and scanning electron micrographs (SEM) to assess particle size distribution homogeneity. The transparency displayed by a supplier who could provide XRD and SEM analyses with their attendant raw results is laudable for quality assurance.
5. Quantitative Supplier Evaluation
The choice of the supplier should move from perceptions or mere pricing negotiations. There is an even more objective manner in which a weighted scoring system is employed to make a choice, whose objectivity is verifiable. Among the factors influencing multiple weighting in the preference for each supplier are regulatory factors, control over purity, documentation quality, eco-friendliness, and sustainability.
Figure 1 illustrates an example comparison of three suppliers using the system. Supplier C is the overall top performer in quality, particularly in purification control and documentation. Figure 2 continues to compare the suppliers across categories to gauge their strengths and weaknesses.
Figure 1. Weighted Total Supplier Scores (Example)
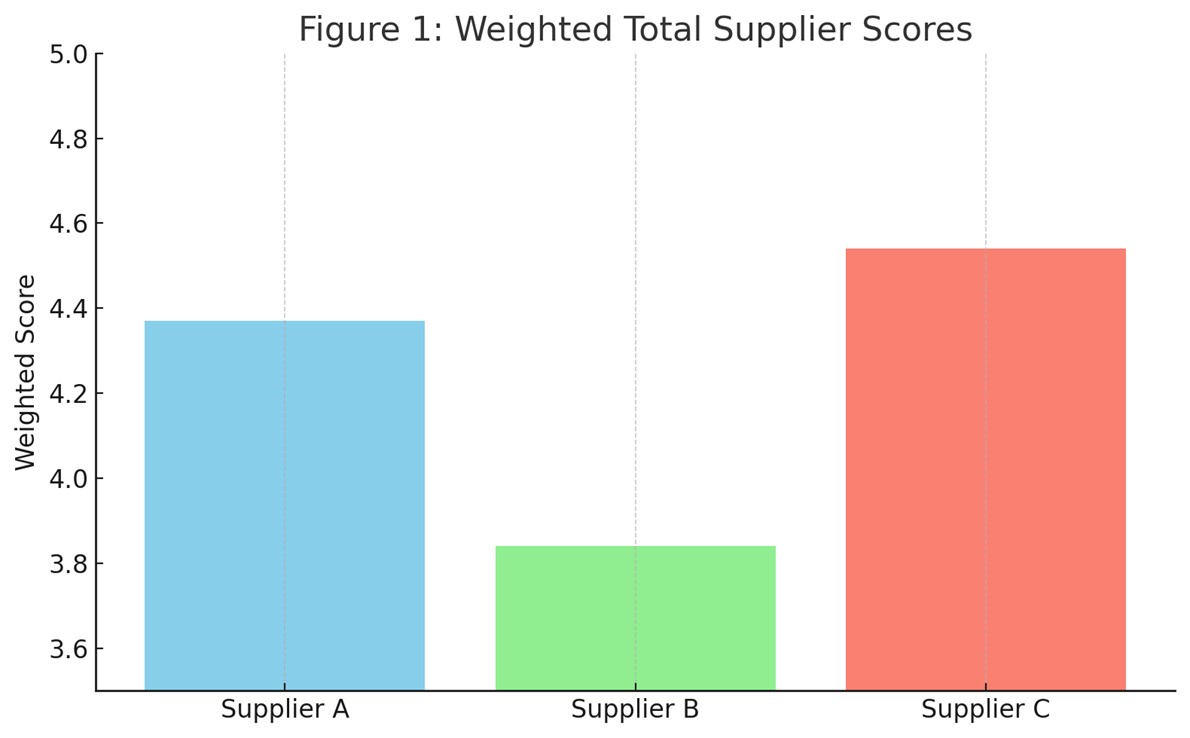
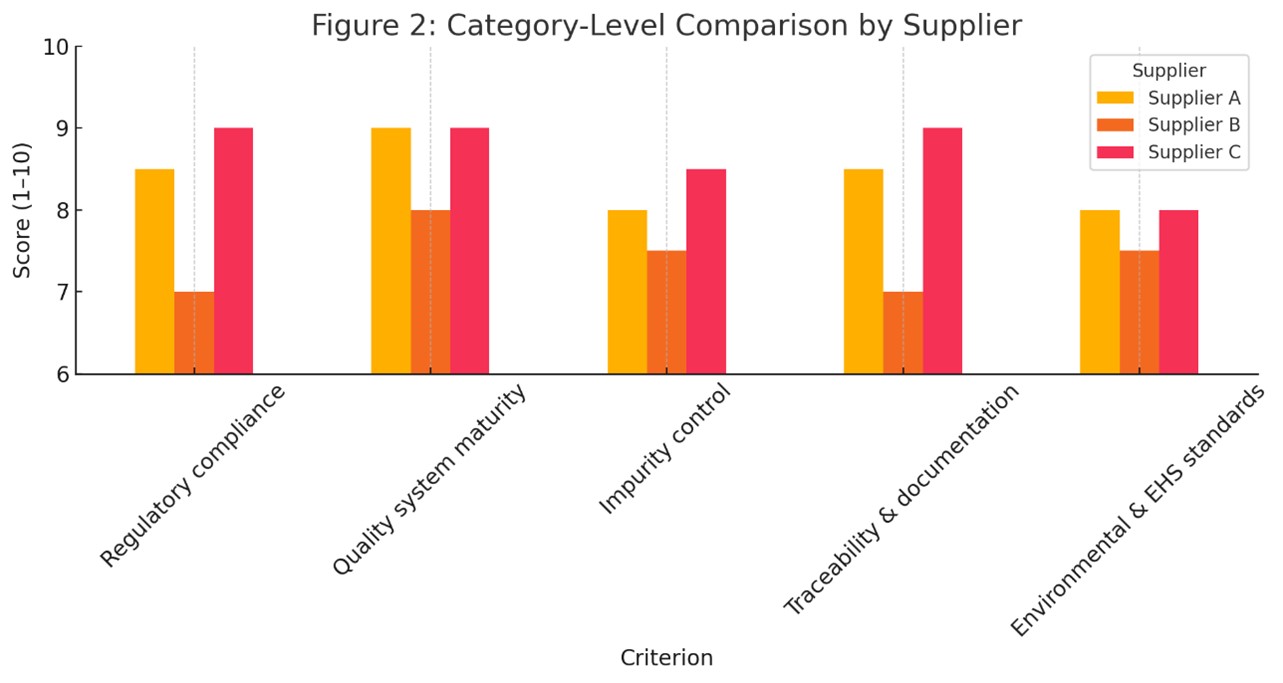
Figure 2. Category-Level Comparison by Supplier
As illustrated in Table 2, an evaluation matrix is used, where weighted totals represent the relative performance of the suppliers. The evaluation matrix enables the reduction of complex quality information into a single, easily auditable quality metric within procurement departments.
Table 2. Example Supplier Scoring Matrix (Extract)
| Criterion | Weight | Supplier A | Supplier B | Supplier C |
| Regulatory compliance | 0.12 | 8.5 | 7.0 | 9.0 |
| Quality system maturity | 0.10 | 9.0 | 8.0 | 9.0 |
| Impurity control | 0.12 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
| Traceability & documentation | 0.10 | 8.5 | 7.0 | 9.0 |
| Environmental & EHS standards | 0.08 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 8.0 |
| Weighted total score | — | 8.54 | 7.75 | 8.75 |
6. Documentation, Compliance, and Sustainability
Regulatory documentation completes the due diligence process. Suppliers should provide up-to-date CoAs, validation summaries, and declarations referencing USP, FCC, ISO 22716, or ASTM D79, depending on the grade. For EU markets, ensure coverage under REACH, including disclosures for nanoforms where relevant.
Sustainability quality certification ISO 14001 is used to demonstrate responsible practices towards the environment, making it suitable for use in an ESG report; other forward-looking suppliers have, in their own initiatives, started adopting low-carbon processes in addition to waste-minimization strategies.
7. Price Versus Total Cost of Ownership
If pricing is considered significant, it is not always the case that the lowest-priced zinc oxide is the most economically viable in the long run. Lack of quality control, batch production, absence of governmental regulation, or poor technical service could lead to high-end costs associated with product failures/reformulations. Considering the total cost of ownership (TCO), including testing costs, time to receive supplies, and sustainability, helps understand the supplier’s long-term value for money.
8. Conclusion
Choosing a zinc oxide supplier is more than deciding on specs and discussing pricing; it is a complex evaluation of quality, compliance, and trustworthiness. By emphasizing respected standards, testing for purity/particle levels, and rating suppliers using complex scoring systems, companies can feel confident in the quality of the zinc oxide they purchase. Of course, the top suppliers make their processes completely transparent, hold international certifications for their quality levels, and also serve their sustainability goals.

