
Can Zinc Oxide and Mineral-Based Sunscreens Be Used on Sensitive Skin?
For individuals with sensitive skin, buying sunscreens can prove to be a gamble. This is mainly because, upon application, many chemical sunscreens tend to irritate, burn, or cause redness on sensitive skin. Dermatologists have relied on mineral sunscreens, particularly zinc oxide, for sensitive skin individuals for the past decade, and the reasons for using them lie in how sunscreens for sensitive skin perform differently.
1. How Mineral and Chemical Sunscreens Differ
Sunscreens shield the skin from the sun’s harmful UV rays, but each type does so differently.
Chemical sunscreens, made from ingredients like oxybenzone, avobenzone, or octocrylene, absorb UV rays and produce a small amount of heat. To be effective, chemical sunscreens must reach the upper skin level. Skin penetration can sometimes cause irritation or allergic contact dermatitis, especially in people with eczema or rosacea.
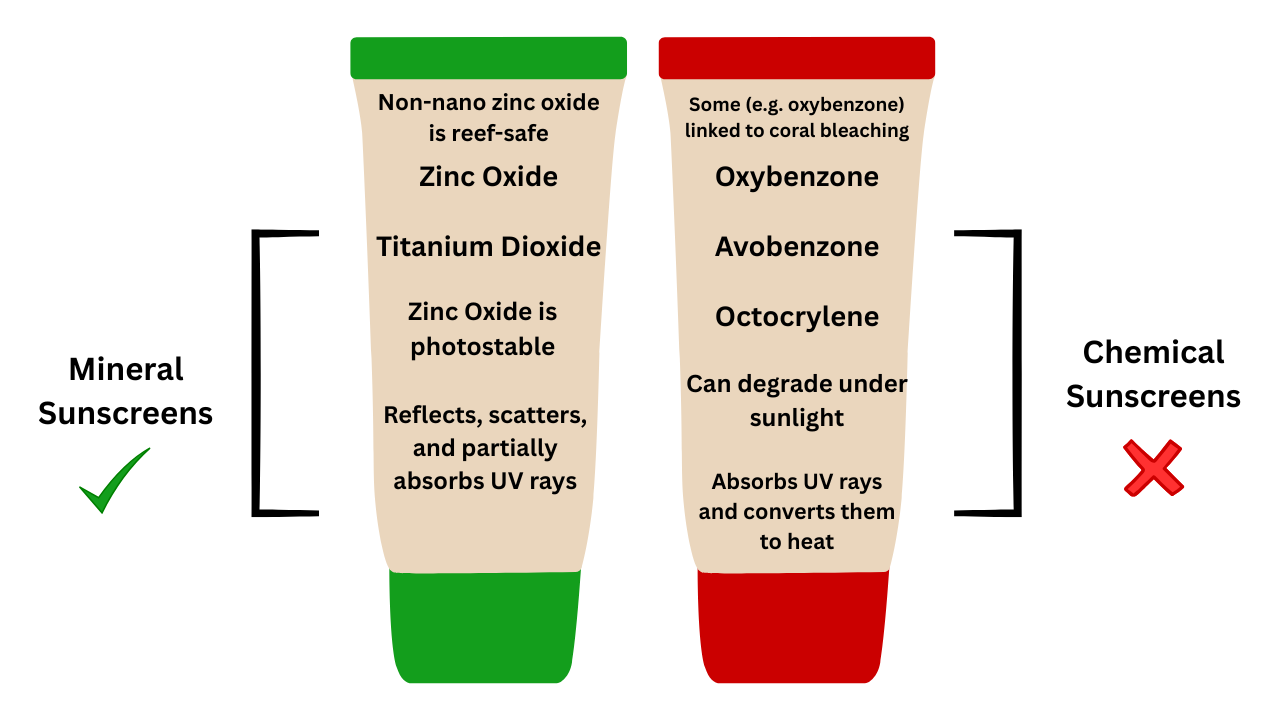
Mineral sunscreens, also known as physical sunscreens, use naturally occurring elements in the form of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. Rather than penetrating, it sits on top of the skin and forms a thin layer that scatters, reflects, and partially absorbs UV rays. The fact that it stays on top also significantly reduces any skin irritation/sensitivity.
Table 1: Comparison of Chemical vs. Mineral Sunscreens
| Feature | Chemical Sunscreens | Mineral Sunscreens (Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide) |
| UV Protection Mechanism | Absorbs UV rays and converts them to heat | Reflects, scatters, and partially absorbs UV rays |
| Common Ingredients | Oxybenzone, Avobenzone, Octocrylene | Zinc Oxide, Titanium Dioxide |
| Skin Penetration | Penetrates upper skin layers | Sits on top of the skin |
| Irritation Risk | Higher (may trigger dermatitis, especially in sensitive skin) | Lower (well-tolerated by sensitive and reactive skin) |
| UVA/UVB Coverage | Depends on formulation | Zinc Oxide: Broad-spectrum; Titanium Dioxide: Primarily UVB |
| Photostability | Can degrade under sunlight | Zinc Oxide is photostable |
| Environmental Impact | Some (e.g. oxybenzone) linked to coral bleaching | Non-nano zinc oxide is reef-safe |
2. Why Zinc Oxide Is Unique
Of the various mineral-based filters, zinc oxide is unique for its broad-spectrum protection. It shields from both UVB rays, which cause sunburn, and from UVA rays, which cause aging and inflammation. With titanium oxide, it is mainly the UVB and short-UVA ranges, so a combination can provide well-rounded protection.
The zinc oxide has a naturally photo-stable structure, such that it does not break down when it comes into contact with sunlight, so it protects the skin for a longer period than many chemical sunscreens. This is important for sensitive skin types that react to the breakdown products of organic molecules.
3. A Soothing Shield for Sensitive Skin
Individuals whose skin is sensitive tend to have a compromised barrier, leading to easy entry for irritants and loss of moisture. The zinc oxide works well in both aims. It does not invade or disrupt the barrier since it stays on its surface, and its gentle anti-inflammatory action can also reduce redness.
The mineral also releases trace zinc ions that support healing and have mild antibacterial activity. That is why zinc compounds appear in diaper creams and acne ointments—they soothe without burning. Patch-testing data consistently show zinc oxide as one of the least sensitizing ingredients in dermatology.
4. Texture, Transparency, and Formulation Advances
The legacy mineral sunscreens used to give a thick white cast, making them difficult to use. This has largely been overcome by using micro-fine and nano-dispersions. The zinc oxide particles, finely milled, can guarantee UV protection without making much difference once it’s mixed.
To enhance glide properties and prevent chalkiness, formulators coat particles with silica or dimethicone. Additionally, for more sensitive skin, it is important to use a fragrance base and an alcohol base, since irritation is caused by additives, and not zinc oxide. The benefit offered by colored mineral sunscreens, which feature iron oxides, helps improve skin tones, in addition to blocking invisible light, which contributes to hyperpigmentation.
5. Evidence From Clinical Research
Dermatological trials regularly demonstrate the superior tolerance of mineral sunscreens. Thus, in a study carried out in 2022 and published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, people with sensitive skin judged zinc oxide-based sunscreens to be more tolerable than both avobenzone and oxybenzone sunscreens.
Professional bodies also confirm similar findings. The American Academy of Dermatology, the National Eczema Association, and the British Association of Dermatologists endorse zinc oxide creams for use on infants, people with eczema, rosacea, and after skin procedures. Pediatricians indicate that 100% zinc creams are their top priority for infants after laser surgery or skin peels because zinc creams protect the skin while still allowing it time to rejuvenate.

6. Titanium Dioxide vs. Zinc Oxide
Titanium dioxide is still a good partner ingredient, but it covers less of the UVA range. It can also create a drier skin finish that tends to feel tight and annoying to sensitive skin types. Of course, zinc oxide, having a more moisturizing and soothing quality, is better suited for sensitive, dry, and irritated skin. Many commercial sunscreens combine both ingredients, using titanium dioxide for its strong UVB protection and zinc oxide for its comprehensive UVA protection [11].
7. Environmental and Ethical Benefits
Mineral sunscreens, apart from being skin-friendly, are also environmentally friendly. Some chemical sunscreens, including oxybenzone and octinoxate, cause coral bleaching, so countries like Hawaii and Palau are banning their use. However, zinc oxide, which is nonnano, is safe for coral reefs and also degradable, causing no harm to any marine life.
The non-volatility and non-bioaccumulative properties of zinc oxide also enable formulators to fulfill low-VOC “clean beauty” requirements. Many organic regulatory organizations, such as COSMOS Natural, include zinc oxide in their lists for approved mineral sunscreens.
8. Tips for Users With Sensitive Skin
- Follow moisturizer. Using a moisturized skin base helps mineral sunscreens apply smoothly and prevents dryness.
- Apply sufficient amounts. The recommended amount is two milligrams per square centimeter, or a fourth teaspoon for face and neck, for rated SPF.
- Reapply every two hours or after swimming or sweating. Although zinc oxide is stable, it can rub off.
- Select formulations that contain tints to avoid white residue and for cosmetic elegance.
- Cleanse gently. Use mild, non-foaming cleansers that will not strip the skin barrier that zinc oxide helps protect.

Through these habits, it is possible for sensitive skin to comfortably coexist with the daily sun protection routine.
9. Future Directions in Mineral Sunscreen Science
Innovations keep perpetually improving the use of zinc oxide for cosmetic and medicinal applications. Scientists are currently designing hybrid nanoparticles that are covered either by plant esters or a silica shell to improve translucency and prevent agglomerations. Other future materials will couple ZnO with antioxidants, vitamin E, or niacinamide to counter free radicals and protect from UV rays.
These enhancements rectify longtime consumer grievances related to weight or whiteness, demonstrating that mineral protection does not have to trade aesthetics for functionality. With increasing consumer interest in gentle, sustainable skin care, zinc oxide’s future applications will only continue to multiply.
10. Conclusion
For sensitive, reactive, or compromised skin, zinc oxide-containing mineral sunscreens are the safest and most reliable choices. The topical protection offered by zinc oxide sunscreens does not allow the skin to undergo penetration, irritation, or chemical degradation. The sunscreens protect the skin from both UVA and UVB rays, reduce inflammation, and are beneficial for the skin barrier, making them suitable for people from infant to adults after surgery. Fragrance and alcohol-free zinc oxide sunscreens can be used on a daily basis.
Amid a crowded shelf of complicated ingredient lists, it’s the ongoing simplicity of zinc oxide that stands as its greatest strength: a mineral barrier that guards the world as well as it guards sensitive skin.

